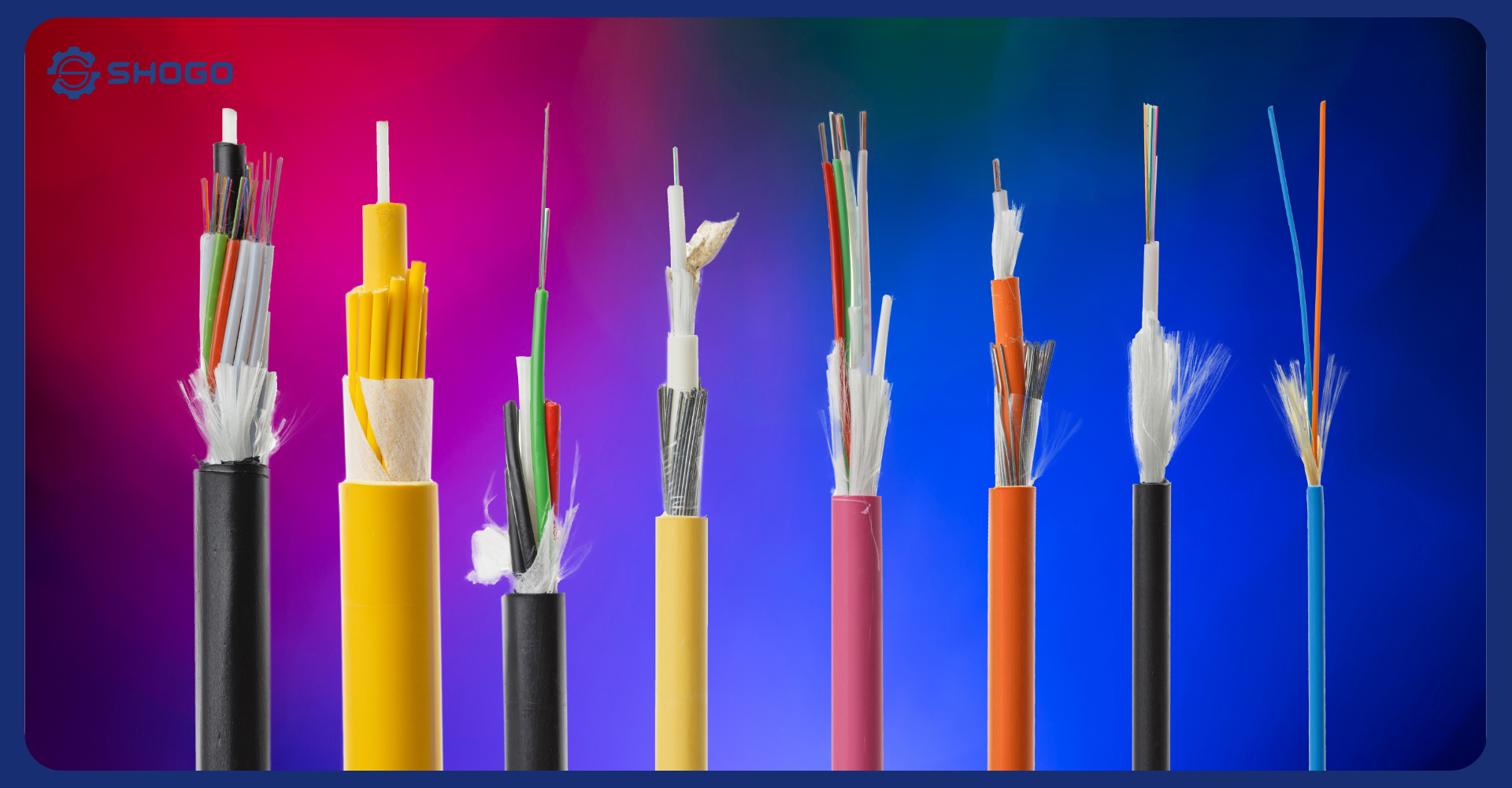
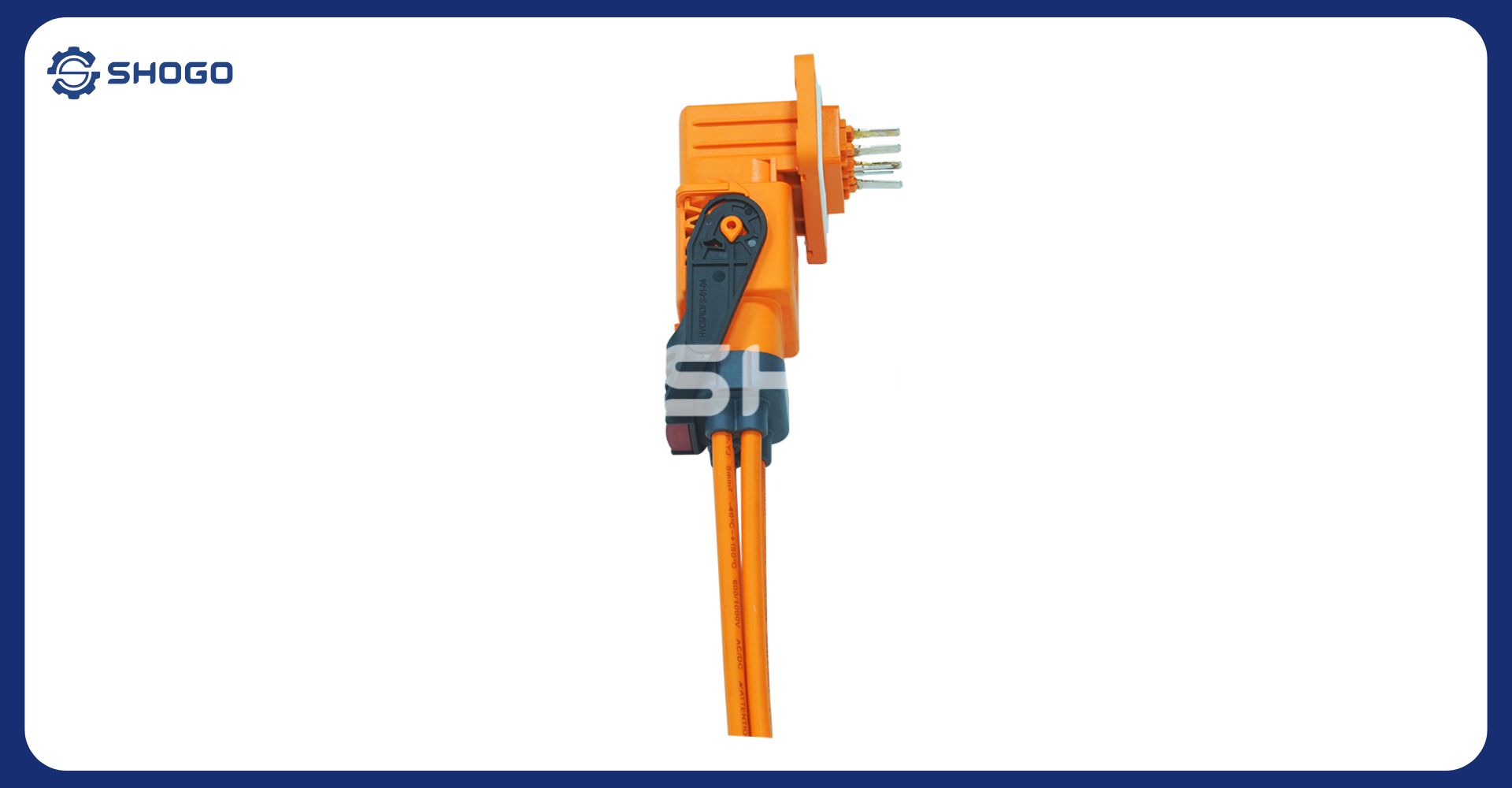
HV Cable plays an important role in the electricity system, transmitting electricity from power plants to consumption areas. Due to their specific nature, high voltage cables are classified according to many different criteria to ensure they meet diverse usage needs and are suitable for different operating conditions. Below is detailed information about how to classify HV CABLE:
1. Classification by structure:
HV Cable structure directly affects the cable’s insulation, load-carrying and operational capabilities. Common types of high voltage power cables are classified according to structure as follows:
- Oil-covered cable: This is a traditional cable that uses many layers of oil-soaked paper to insulate the conductor. The advantage of this type of cable is that it is cheap, easy to produce and repair. However, its disadvantages are that it is bulky, heavy, susceptible to moisture, aging over time and high power loss.
- Synthetic plastic coated cable: This type of cable uses synthetic plastic materials such as XLPE (cross-linked polyethylene), EPR (ethylene propylene synthetic caoutchouc) for insulation. Compared to oil paper coated cables, synthetic plastic coated cables have many outstanding advantages such as: light, flexible, chemical resistant, good fire resistance, low power loss and longer life. The only disadvantage of this type of cable is that the price is higher than oil-paper covered cables.

- Atmospheric cable: This type of cable uses compressed air (usually nitrogen gas or SF6) to insulate the electrical conductors. The advantages of atmospheric cables are compact size, light weight, low power loss and the ability to self-recover after an incident. However, its disadvantages are high cost, need for complex compressed air supply system and regular maintenance.
- Waveguide cable: This type of cable uses electromagnetic waves to transmit electricity instead of using electric current. The advantages of waveguide cables are low power loss, environmental friendliness and the ability to transmit power over long distances. However, its disadvantages are complex production technology, high cost and the need for signal modulators and decoders at both ends of the line.
2. Classification by voltage:
Voltage is the most important factor that determines the structure, insulation ability and application of high voltage cables. Based on voltage criteria, HV Cable is divided into the following types:
- Medium voltage cable: This is a type of cable with voltage from 3 kV to 35 kV. Medium voltage cables are often used in regional power distribution systems, providing power to transformer stations, factories and residential areas.
- High voltage cable: This type of cable has voltages from 35 kV to 500 kV. High voltage cables are used in power transmission systems, transmitting electricity from power plants to regional transformer stations.
- Ultra high voltage cable: This is a type of cable with a voltage of 500 kV or more. Ultra-high voltage cables are used in the national power system, transmitting power over long distances.
3. Classification according to intended use:
The purpose of using high voltage cables also affects the structure, materials and features of the cable. Popular types of high voltage cables according to purpose include:
- HV Cable for electric cars: HV Cable plays an important role in electric cars, responsible for transmitting power from the battery pack to the electric motor and other systems on the vehicle.

- Power cable: This type of cable is used to transmit electricity from power plants to transformer stations and consumption areas. Power cables need to have high load capacity, low power loss and stable operation in harsh environmental conditions.
- Underground cable: This type of cable is buried underground to avoid affecting the environment and landscape. Underground cables need to be waterproof, termite-proof and able to withstand high mechanical pressure.
- Suspension cable: This type of cable is hung on electric poles or trusses, often used for overhead power lines. The cable car needs to be light in weight, have high mechanical strength and be able to withstand wind and snow loads.
- Underwater cable: This type of cable is placed on the bottom of seas or rivers and lakes, often used for inter-island or inter-national power lines. Underwater cables need to be absolutely waterproof, withstand high water pressure and resist corrosion by chemical agents in the water environment.
In addition, HV Cable is also classified according to a number of other criteria such as:
- Number of cores: High voltage cables can have 1 core, 3 cores, 4 cores or more cores, depending on usage needs and transmission capacity.
- Conductive materials: The conductors of high voltage cables are usually made of copper or aluminum. In some special cases, superconducting materials can be used.
- Protective sheath: High voltage cable protective sheath can be made of synthetic plastic, metal or a combination of both materials.
Note:
- HV CABLE classification is for reference only and may vary depending on the manufacturer and applicable standards.
- You should choose the type of HV CABLE that suits your needs and operating conditions to ensure safety and efficiency.
- In addition, other factors should be noted such as: price, brand, warranty when choosing HV CABLE.
Besides information about HV Cable classification, you can also refer to other articles related to this topic such as:
- Benefits of using HV Cable
- Factors to keep in mind when choosing HV Cable
- Instructions for installing HV Cable
- Answers to frequently asked questions about HV Cable
Classifying HV Cable according to structure, voltage, and intended use is necessary to select the appropriate cable type for use and operating conditions. Choosing HV CABLE properly will ensure safety, efficiency and cost savings for the electrical system.
Hopefully the detailed information about HV Cable classification presented in this article will help you better understand this topic.


