1. Introduction
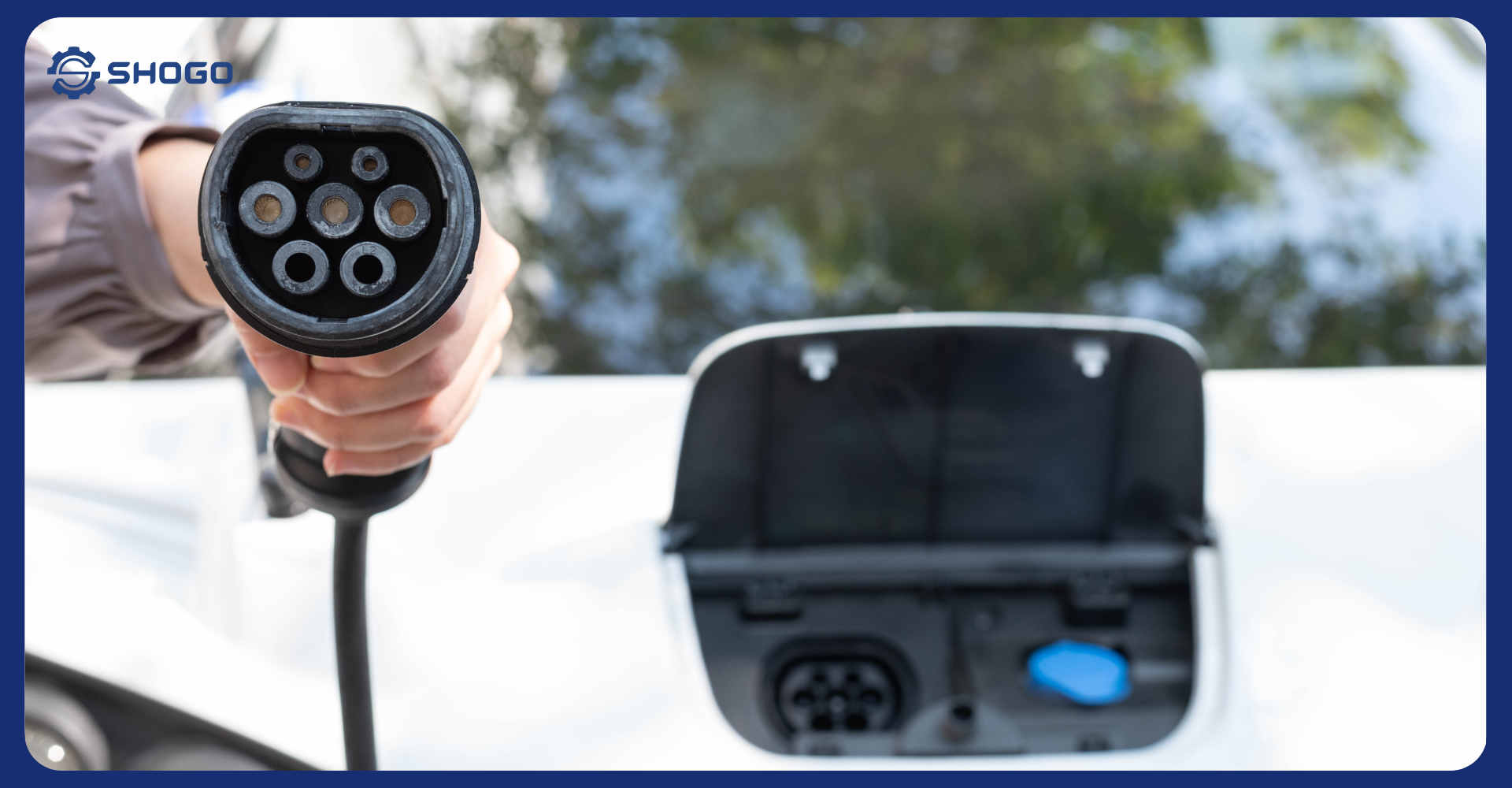
In the electrical system of electric vehicles, High Voltage Cables play a crucial role in transmitting energy from the battery to the motor and other components. To ensure stable operation, safety, and minimize electromagnetic interference, designing a shielding system for electrical cables is essential.
Shielding design includes:
- Shielding High Voltage Cables
- Shielding the connection between High Voltage Cables and connectors
- Shielding High Voltage Cables
2. Role of Shielding Design
2.1. Ensuring User Safety
- Preventing electric shock: High Voltage Cables carry a large amount of electrical energy. If not properly insulated and protected, technicians or vehicle maintenance personnel may be electrocuted when coming into direct contact. Insulation and shielding layers prevent current leakage, ensuring user safety.
- Preventing fire and explosion: When a cable is exposed or short-circuited, it can generate sparks and high heat, easily causing fires and explosions. Shielding design protects the cable from external influences, minimizing the risk of fire and explosion.
2.2. Protecting the Electrical System
- Preventing short circuits: Environmental factors such as humidity, high temperature, or mechanical impacts can damage the cable’s insulation, causing short circuits. Shielding design protects the cable from these impacts, ensuring the stability of the electrical system.
- Reducing electromagnetic interference: High Voltage Cables generate strong magnetic fields, which can interfere with other electronic devices in the vehicle. A conductive shielding layer helps reduce the dispersion of magnetic fields, protecting other electronic devices from interference.
2.3. Enhancing Durability and Lifespan
- Protecting cables from mechanical impacts: High Voltage Cables are often located in areas that are susceptible to impact or abrasion. The protective sheath enhances the cable’s durability, preventing damage from mechanical impacts.
- Preventing corrosion: Cables are exposed to the vehicle’s interior environment, which can have high humidity or chemicals. The protective sheath prevents cable corrosion, extending the system’s lifespan.
2.4. Improving Operational Performance
- Reducing energy loss: Shielding design helps minimize heat dissipation, thereby reducing energy loss and increasing the electrical system’s operating efficiency.
- Enhancing conductivity: High-quality insulation reduces resistance, enhancing current conductivity and ensuring sufficient energy supply to the motor.
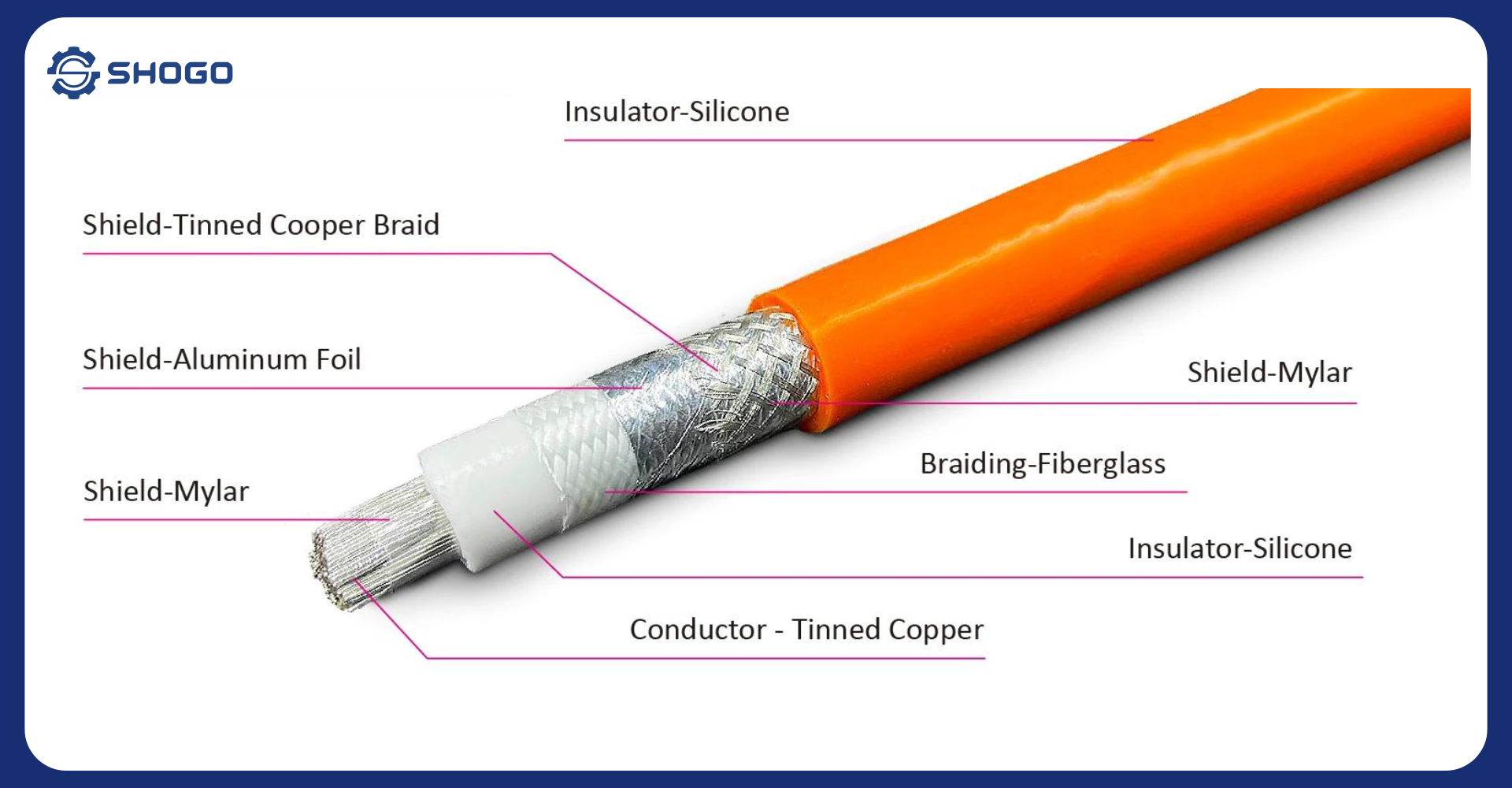
3. Shielding of High-Voltage Cables
High Voltage Cables primarily consist of four parts: conductor, insulation, shield, and jacket. The cable shield is responsible for preventing electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI). It also prevents leakage currents generated between adjacent cables. Therefore, it plays a very important role in cable design.
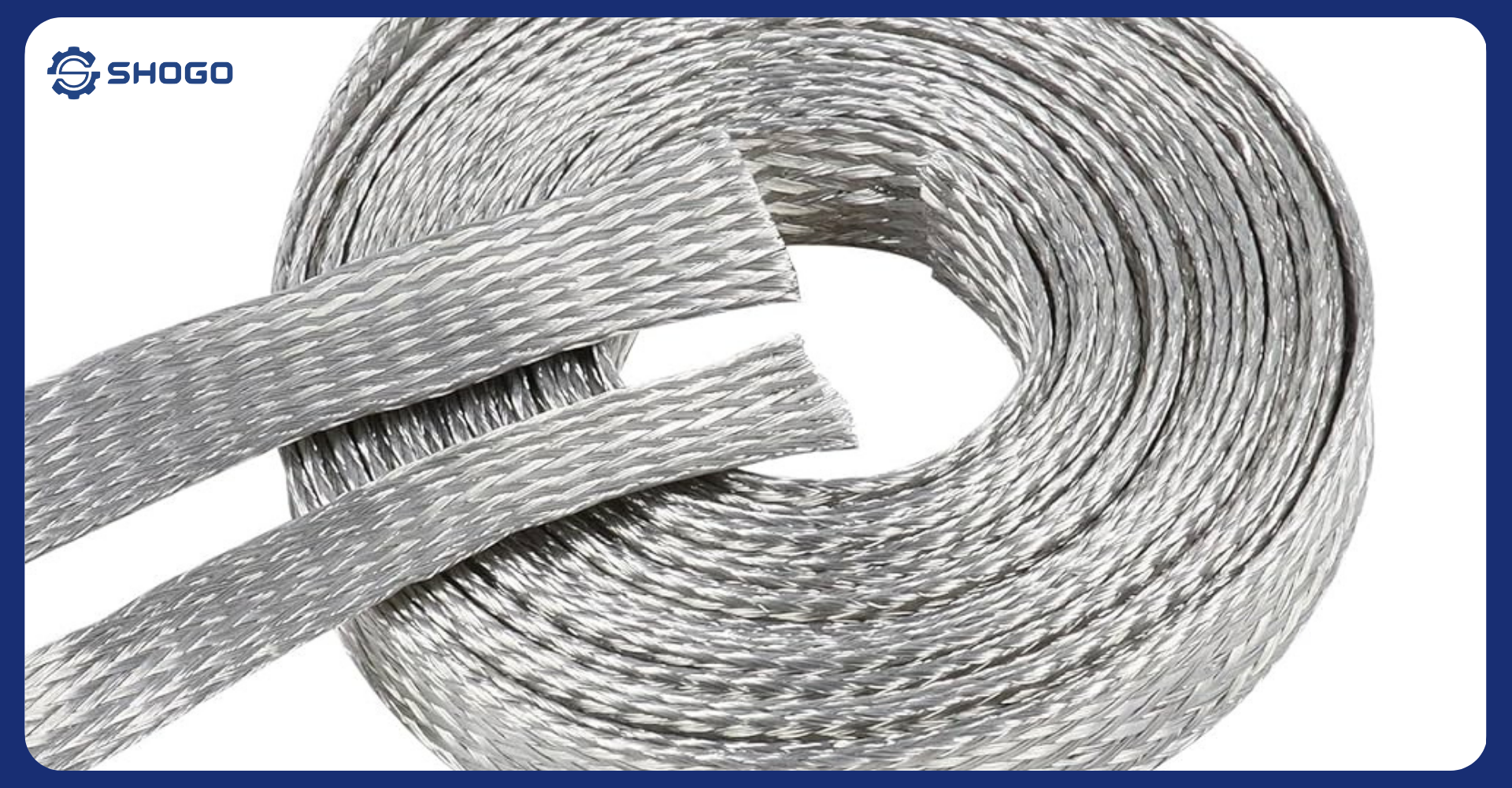
The structure of the High Voltage Cables shield is typically divided into two types: tinned copper braided shield and aluminum foil shield.
3.1. Tinned Copper Braided Shield

It has good EMI shielding performance. The braided shield provides excellent protection against both high and low-frequency interference while maintaining good winding and bending life. The braided shield typically contains two sets of copper strands, braided in opposite directions. Due to this design, the braided shield has good winding properties. Most cables using braided shields specify a coverage range of 80% to 95%. The higher the coverage of the braid, the better the EMI shielding effectiveness.
Roles of the tinned copper braid:
- Shielding against electromagnetic interference
- Eliminating the shielding effect of the surface potential of high-voltage cables and eliminating induced electricity
- Protective shielding function. The copper braid is braided outside the main core insulation and is in good contact with the ground core, which can respond promptly to leakage situations
3.2. Aluminum Foil Shield

The metal foil shield consists of metal foil, usually aluminum foil, which is rolled into a thin polyester or polypropylene film. It is typically wrapped around the cable core in overlapping layers.
The aluminum foil shield provides 100% coverage. 100% coverage is only a physical property and does not mean that the metal foil shield can shield 100% of electromagnetic interference. It is very effective in shielding both high and low-frequency interference. They are lighter, less bulky, and often reduce the cost of the cable assembly or wire compared to braided shields.
The core conductors are often coated with one or two layers of thin aluminum foil tape as an outer sheath to ensure that the electrical properties meet UL standards and have a braided shield on the outside. This is a combined shield. The combined shield contains multiple shields or uses multiple shielding methods, with higher performance over a wider frequency spectrum. At the same time, it also plays an important role in preventing moisture from entering the insulation material of the inner conductor during use.
Roles of the aluminum foil shield:
- Protection against electromagnetic interference as in the braided shield
- Prevents moisture and water vapor from entering the cable core from the outside environment.
- Additionally, it plays an important role in improving mechanical properties such as bending resistance and tensile strength of the cable; therefore, it must be used correctly according to the relevant technical parameters.


